 |
| ArcView |
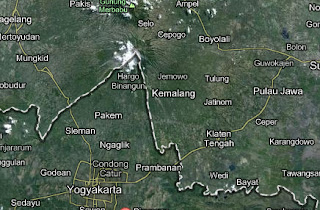
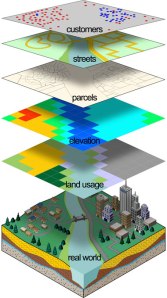
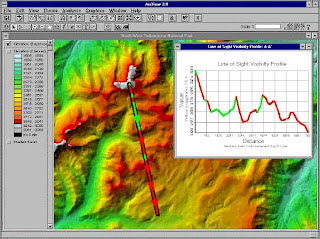
ArcView is one geographic information system software (GIS) created by ESRI (Environmental Systems Research Intitute). ArcView can perform data exchange, mathematical operations, spatial and attribute information displays simultaneously, create thematic maps, providing programming language (script), and perform other special functions with the help of extensions.
ArcView Shapefile format can be read, but it can keep calling ArcView data format BSQ, BIL, BIP, JPEG, TIFF, BMP, GeoTIFF or grid data from ARC / INFO and many other data. Each spatial data called will appear as a Theme and a combination of theme-theme will appear in a view. ArcView organize the components of the program (view, themes, tables, charts, layouts, and scripts) in a project. Project is an organizational unit of the highest in the ArcView.
ArcView 8.x and 9.x are part of the ArcGIS Desktop software suite. All components are installed on the system, with only those that are licensed being made functional. The current version of ArcView sold by Esri is 10.
Download software:
http://www.esri.com/products
Download for free (copy this link to browser) :
http://www.4shared.com/zip/Nk2G6gCR/arcview_gis_33.html