Geographic Information System (GIS) is an information system designed to work with spatially referenced data or berkoordinat geography. In addition, GIS can also combine data, organize the data and perform data analysis that will produce output that can be used as a reference in decision-making on issues related to geography.
Understanding GIS today is more often applied to the spatial or geographic information technologies oriented to the use of computer technology. The correct combination of the four main components will determine the success of a development project Geographic Information Systems.The main components of Geographic Information Systems can be divided into 4 main components: hardware (digitizer, scanner, Central Procesing Unit (CPU), hard disk, etc.), software (ArcView, Idrisi, ARC / INFO, ILWIS, MapInfo, etc.), organization (management) and user (user).
Geographic Information Systems are divided into two groups: manual systems (analog), and automated systems (digital-based computers). The difference lies in the way of management. Information systems are usually manually merge some data such as maps, transparencies for stacks (overlay), aerial photography, statistical reports and reports of field surveys. All of the data is compiled and analyzed manually. While automated Geographic Information Systems has been using the computer as a data processing system through a digital process.
GIS applications can be used for various purposes for which the data is processed has geographic references, meaning the data is composed of the phenomenon or object that can be presented in a physical form and spatial location (Indrawati, 2002).
The main objective of the use of Geographic Information Systems is to make it easier to get the information that has been processed and stored as an attribute of a location or object. The main characteristic of data that can be used in Geographic Information Systems is the data that has been tied to the location and a basic data that has not been specified (Dulbahri, 1993).
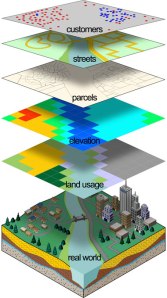
The data are processed in GIS is basically composed of spatial data and attribute data in digital form, so that the analysis can be used is the analysis of spatial and attribute analysis. Spatial data is data relating to the spatial location of the general shape of the map. While attribute data is a data table that serves to explain the existence of various objects as spatial data.
The presentation of spatial data has three basic ways, namely in the form of dots, lines and shapes form area (polygon). The point is a single appearance of a pair of x, y coordinates showing the location of an object such as height, location of the city, the location of the sample and the others. The line is a set of points which form an elongated appearance such as rivers, roads, and other kontus. While the appearance of the area is bounded by a line that forms a homogeneous space, for example: boundary, limit the use of land, islands, and so forth.
Spatial data structure divided into two raster data models and data models vector. Raster data is data that is stored in a rectangular box (grid) / cell, forming an orderly space. Vector data is data that is recorded in the form that displays the coordinates of the point, placing and storing spatial data using point, line or area (polygon) (Barus and Wiradisastra, 2000)















0 komentar:
Posting Komentar